TimeGPT Quickstart (Polars)
TimeGPT is a production ready, generative pretrained transformer for time series. It’s capable of accurately predicting various domains such as retail, electricity, finance, and IoT with just a few lines of code 🚀.
Step 1: Create a TimeGPT account and generate your API key
- Go to dashboard.nixtla.io
- Sign in with Google, GitHub or your email
- Create your API key by going to ‘API Keys’ in the menu and clicking on ‘Create New API Key’
- Your new key will appear. Copy the API key using the button on the right.

Step 2: Install Nixtla
In your favorite Python development environment:
Install nixtla with pip:
pip install nixtla
Step 3: Import the Nixtla TimeGPT client
from nixtla import NixtlaClient
You can instantiate the NixtlaClient class providing your authentication API key.
nixtla_client = NixtlaClient(
api_key = 'my_api_key_provided_by_nixtla'
)
Check your API key status with the validate_api_key method.
nixtla_client.validate_api_key()
True
This will get you started, but for more secure usage, see Setting Up your API Key.
Step 4: Start making forecasts!
Now you can start making forecasts! Let’s import an example using the classic AirPassengers dataset. This dataset contains the monthly number of airline passengers in Australia between 1949 and 1960. First, load the dataset and plot it:
import polars as pl
df = pl.read_csv(
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Nixtla/transfer-learning-time-series/main/datasets/air_passengers.csv',
try_parse_dates=True,
)
df.head()
| timestamp | value |
|---|---|
| date | i64 |
| 1949-01-01 | 112 |
| 1949-02-01 | 118 |
| 1949-03-01 | 132 |
| 1949-04-01 | 129 |
| 1949-05-01 | 121 |
nixtla_client.plot(df, time_col='timestamp', target_col='value')

Data Requirements
- Make sure the target variable column does not have missing or non-numeric values.
- Do not include gaps/jumps in the timestamps (for the given frequency) between the first and late timestamps. The forecast function will not impute missing dates.
- The time column should be of type Date or Datetime.
For further details go to Data Requeriments.
Forecast a longer horizon into the future
Next, forecast the next 12 months using the SDK forecast method. Set the following parameters:
df: A pandas DataFrame containing the time series data.h: Horizons is the number of steps ahead to forecast.freq: The polars offset alias, see the possible values here.time_col: The column that identifies the datestamp.target_col: The variable to forecast.
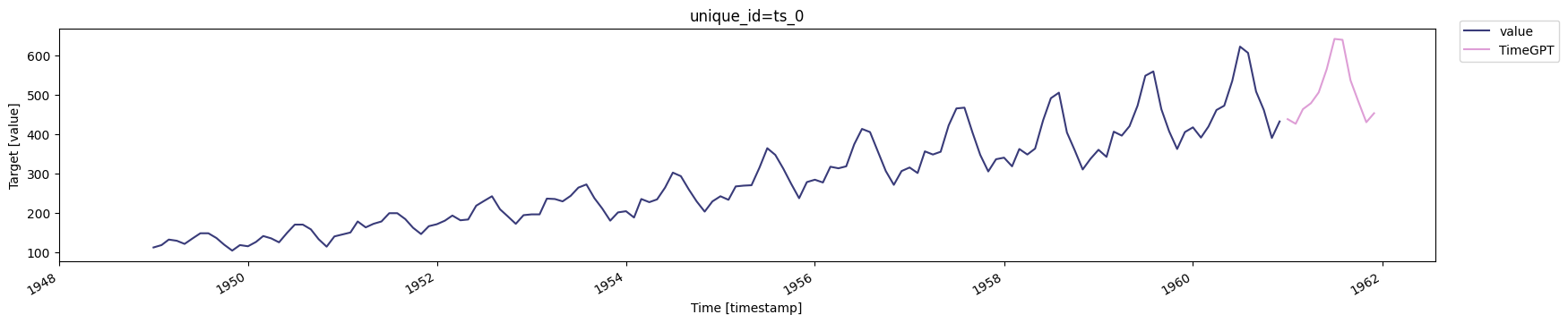
timegpt_fcst_df = nixtla_client.forecast(df=df, h=12, freq='1mo', time_col='timestamp', target_col='value')
timegpt_fcst_df.head()
INFO:nixtla.nixtla_client:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtla.nixtla_client:Querying model metadata...
INFO:nixtla.nixtla_client:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtla.nixtla_client:Restricting input...
INFO:nixtla.nixtla_client:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
| timestamp | TimeGPT |
|---|---|
| date | f64 |
| 1961-01-01 | 437.837921 |
| 1961-02-01 | 426.062714 |
| 1961-03-01 | 463.116547 |
| 1961-04-01 | 478.244507 |
| 1961-05-01 | 505.646484 |
nixtla_client.plot(df, timegpt_fcst_df, time_col='timestamp', target_col='value')
You can also produce longer forecasts by increasing the horizon parameter and selecting the timegpt-1-long-horizon model. Use this model if you want to predict more than one seasonal period of your data.
For example, let’s forecast the next 36 months:
timegpt_fcst_df = nixtla_client.forecast(df=df, h=36, time_col='timestamp', target_col='value', freq='1mo', model='timegpt-1-long-horizon')
timegpt_fcst_df.head()
INFO:nixtla.nixtla_client:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtla.nixtla_client:Querying model metadata...
WARNING:nixtla.nixtla_client:The specified horizon "h" exceeds the model horizon. This may lead to less accurate forecasts. Please consider using a smaller horizon.
INFO:nixtla.nixtla_client:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtla.nixtla_client:Restricting input...
INFO:nixtla.nixtla_client:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
| timestamp | TimeGPT |
|---|---|
| date | f64 |
| 1961-01-01 | 436.843414 |
| 1961-02-01 | 419.351532 |
| 1961-03-01 | 458.943146 |
| 1961-04-01 | 477.876068 |
| 1961-05-01 | 505.656921 |
nixtla_client.plot(df, timegpt_fcst_df, time_col='timestamp', target_col='value')

Produce a shorter forecast
You can also produce a shorter forecast. For this, we recommend using the default model, timegpt-1.
timegpt_fcst_df = nixtla_client.forecast(df=df, h=6, time_col='timestamp', target_col='value', freq='1mo')
nixtla_client.plot(df, timegpt_fcst_df, time_col='timestamp', target_col='value')
INFO:nixtla.nixtla_client:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtla.nixtla_client:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtla.nixtla_client:Restricting input...
INFO:nixtla.nixtla_client:Calling Forecast Endpoint...

Updated 5 months ago